Information
Authors: Robert Goldstein, Robert Cryderman
Location/Venue: UIE Congress Hannover, Germany
Overview
- Market Demands for New Product Development
- Advantages/Drawbacks of Induction Heat Treating Compared to Other Methods
- Tools Available for Material Characterization
- Opportunities for Improved Measurement Methods
- Conclusions
Market Demands
- Lighter
- Stronger
- Cleaner
- Cheaper
- Quicker to Market
Due to Unique Features of Induction Heating, We Have a Better Opportunity to Be Magicians than Other Technologies
Specific Features of Induction Heating
- Heat generation occurs inside the part
- Heating is contactless
- Method can provide very high power densities
- Any processing atmosphere (air, protective gas, vacuum)
- Very high temperatures may be created
- Heating may be highly selective in the depth and along the surface - Very Important Feature, especially for multi-material components
Advantages of Induction Heating
- Short heating cycles and high production rates
- Electromagnetic forces can be used in combination with heating to stir or contain molten metal
- Better metallurgical results due to fast and clean heating
- Energy savings due to selectivity and high efficiency
- Good control and repeatability
- Minimal or no surface oxidation and decarburization
- Lower distortions for surface or local hardening
- Favorable Distributions of Residual Stresses (Better loading capability)
- Much less Alloy Required (lower cost)
- Finer Grain Structures Possible
- Favorable for industrial environment (in-line heating, no pollution, “push button” performance)
- Some processes may not be accomplished other than by induction
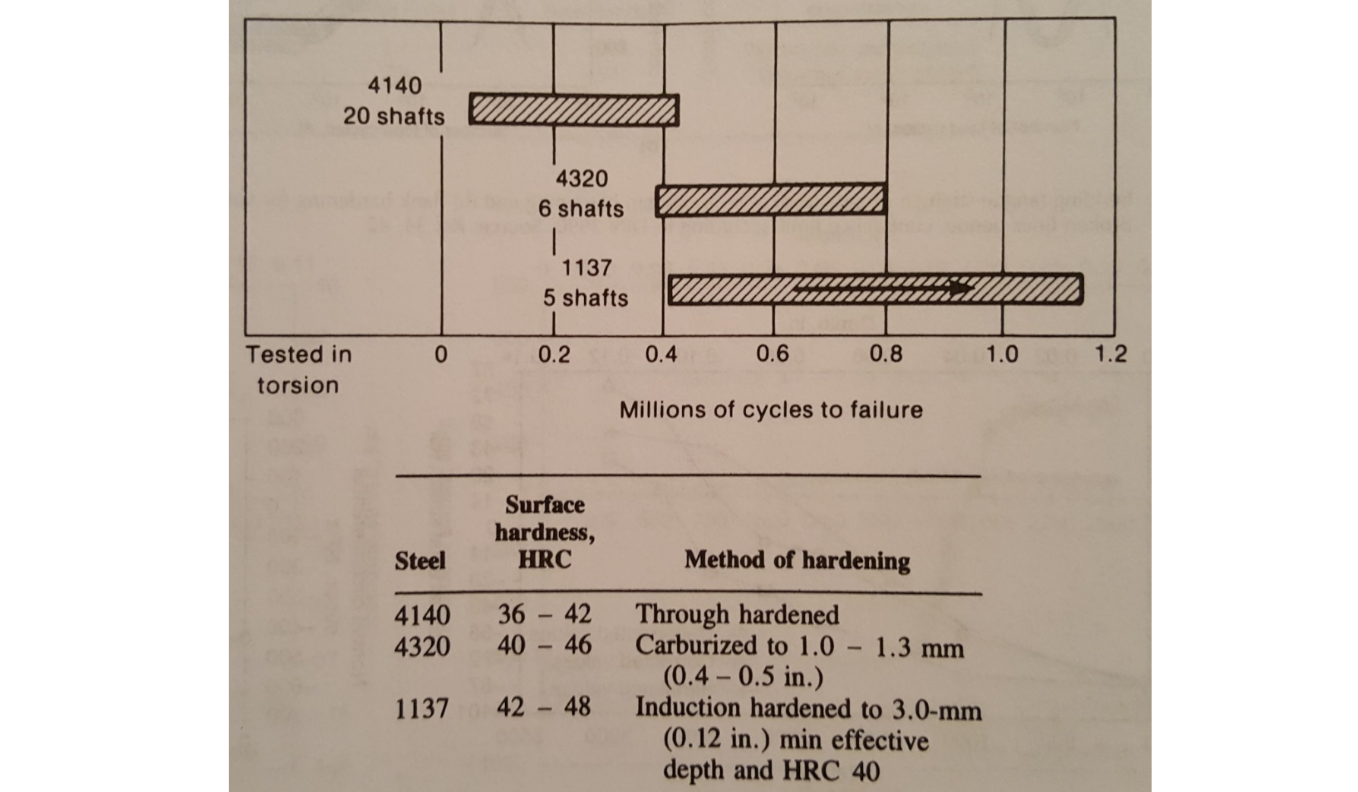
Comparison of Through, Case and Induction Hardened Fatigue Life for Transmission Shafts
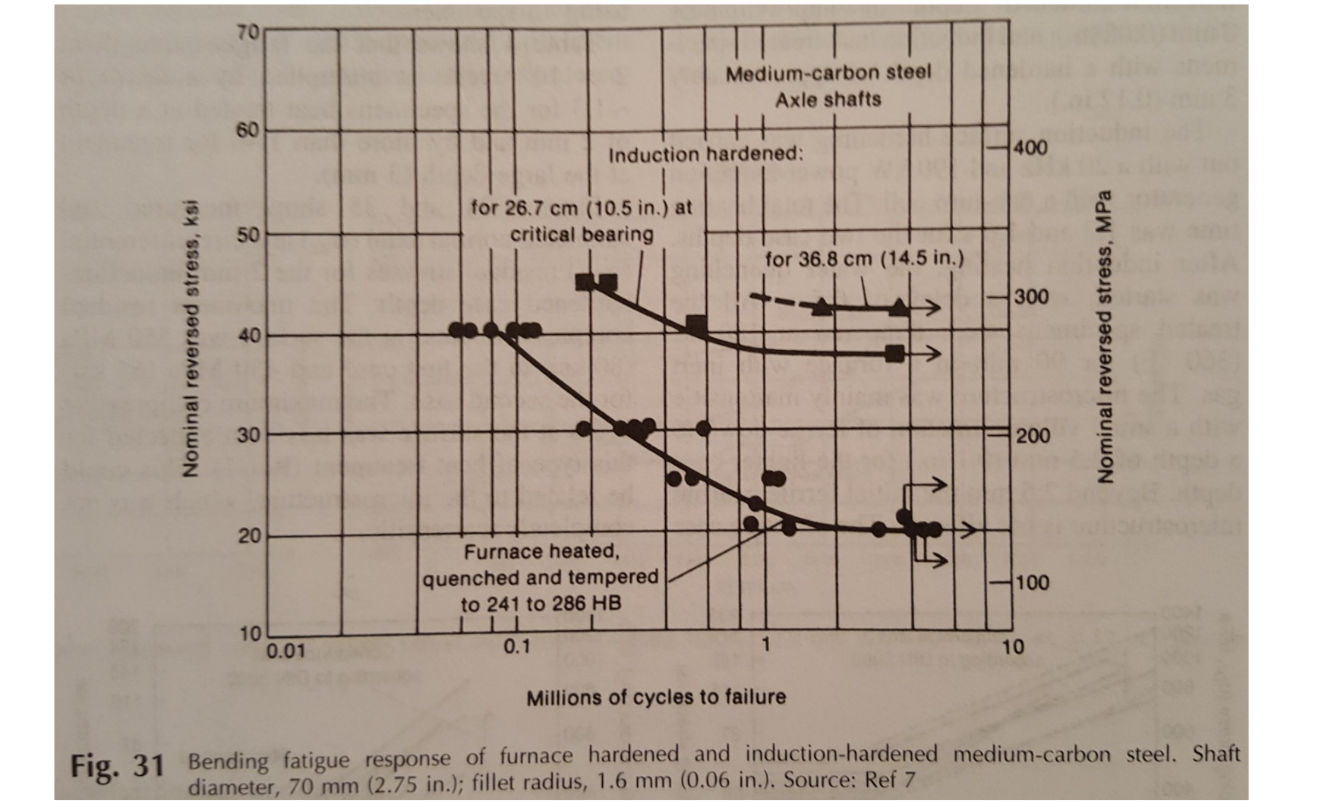
Comparison of Through and Induction Hardened Bending Fatigue
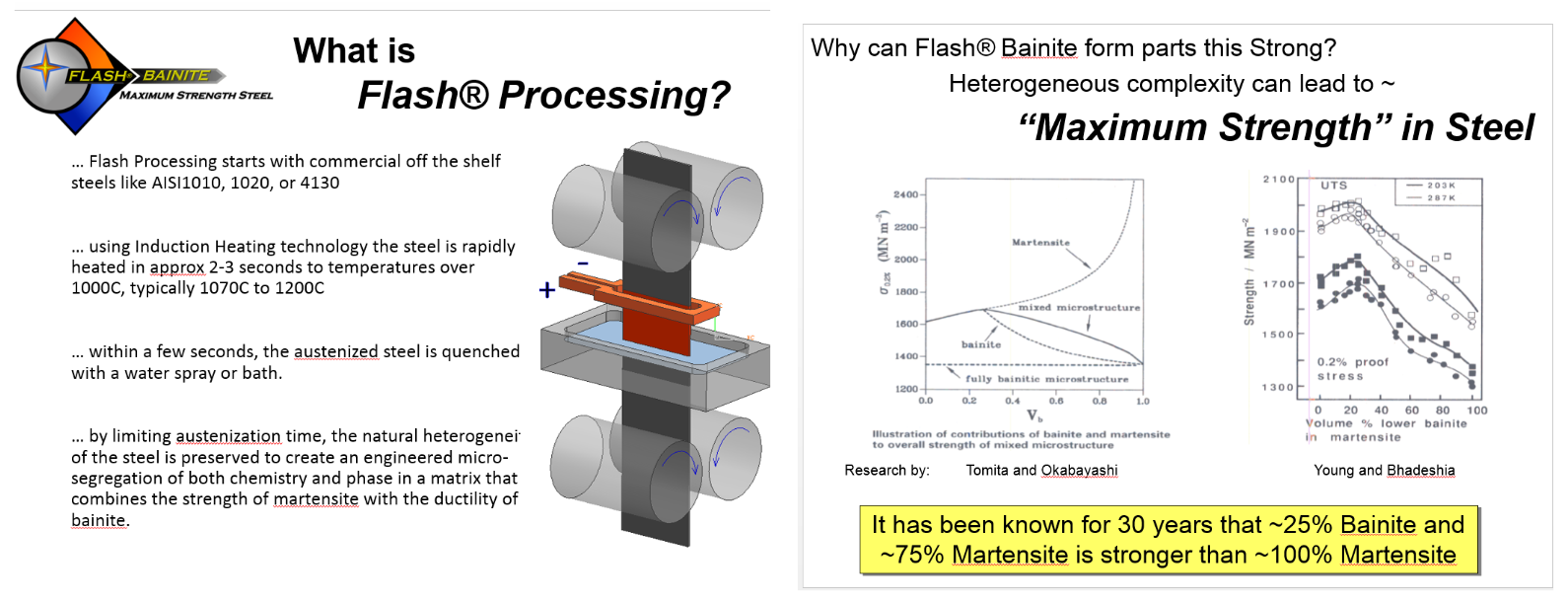
Improved Mechanical Properties Possible when Using Non-Equilibrium Structures
Cold Formed AHSS Components

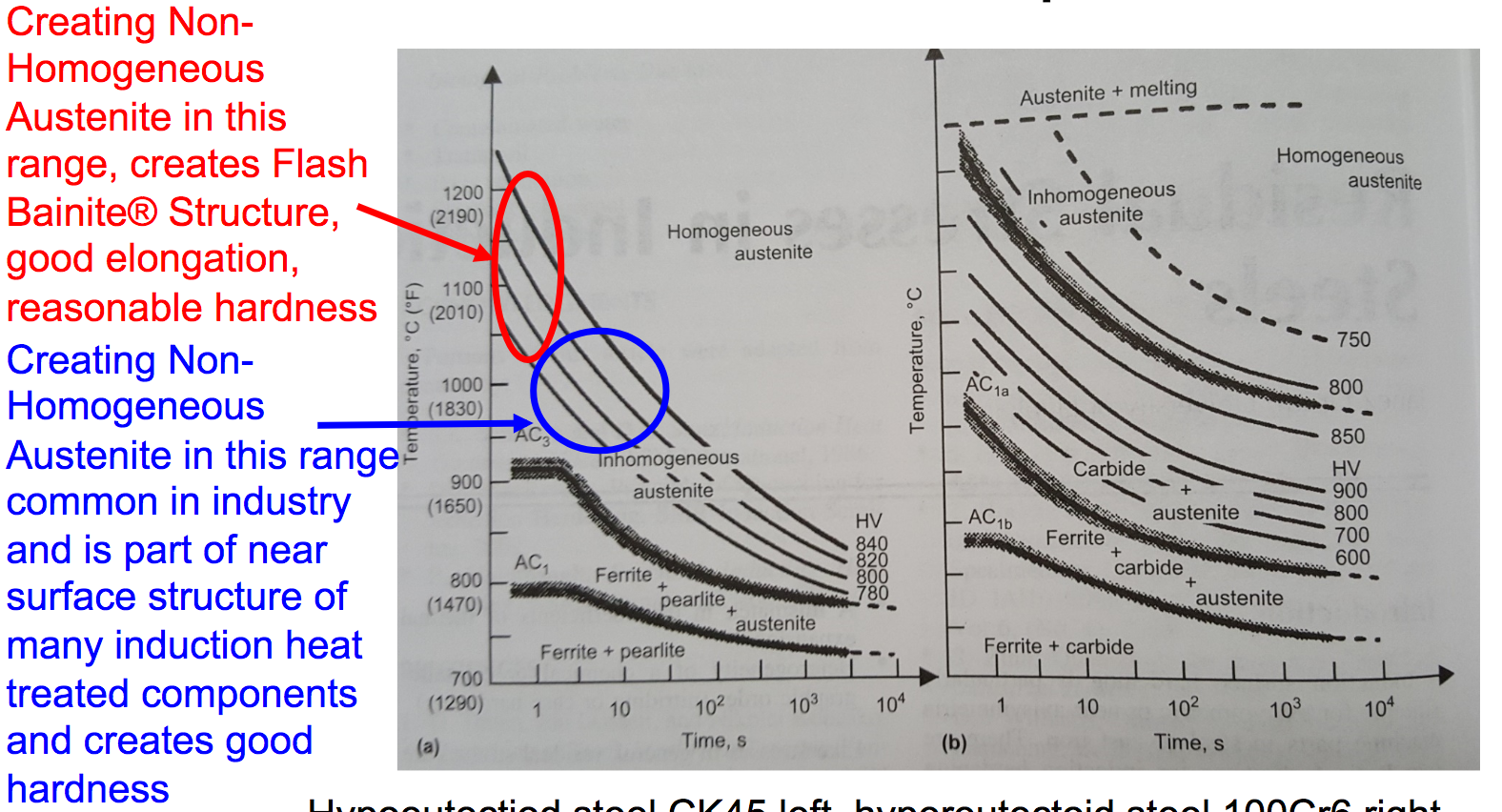
Effect of Short Time Heat Treatment on Transformation Temperature
Drawbacks of Induction Heat Treating
- Process is more complicated than furnace heat treatment (more variables), and empirical development can be challenging
- Product Designers Do Not Understand the Process
-
Limited Materials Database
- Even more limited understanding of tempering and other sub-critical processes such as rapid spherodization developed by COMTES

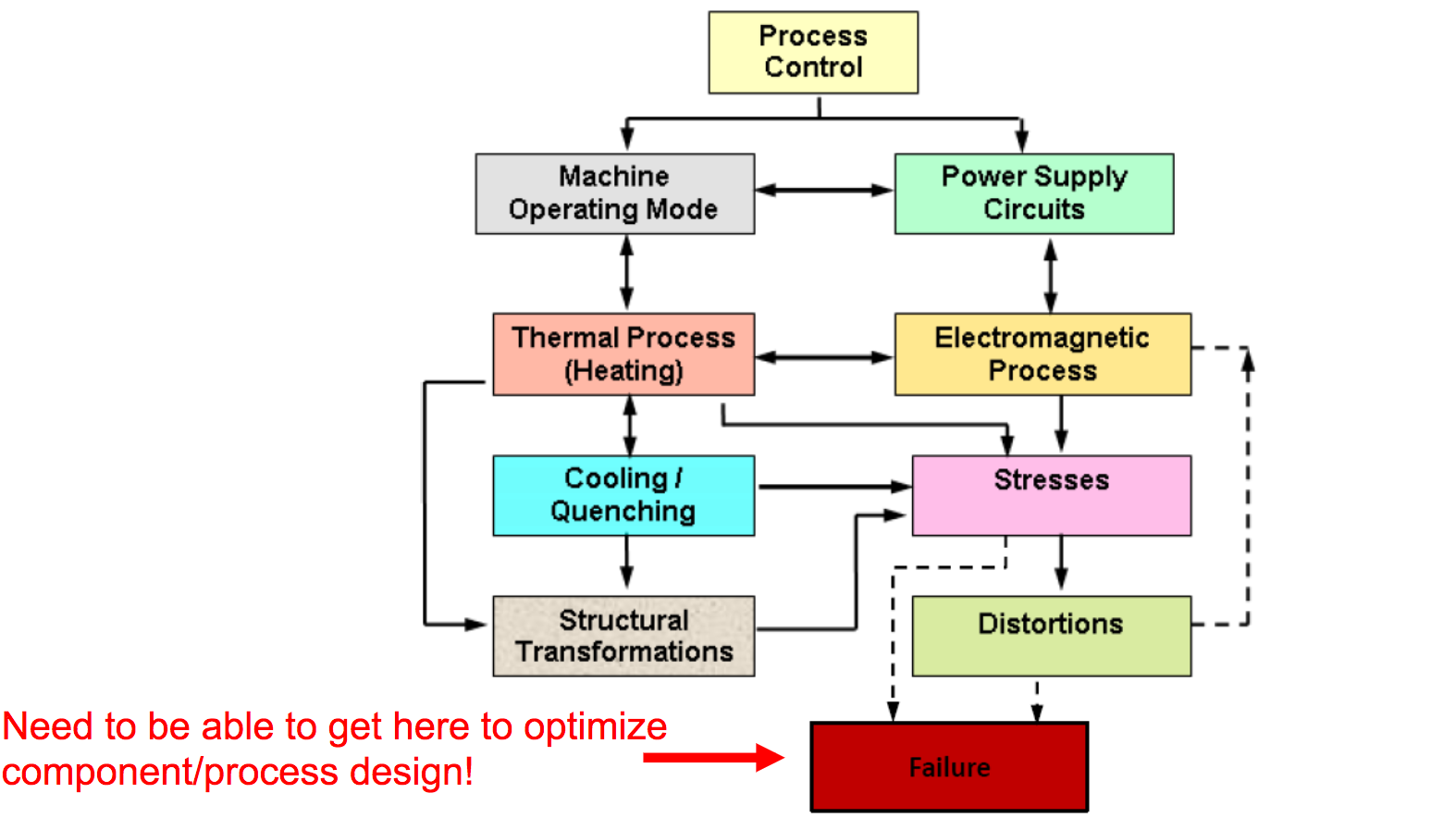
Mutually Coupled Phenomena in Induction Heating Process
Tools Available for Materials Response Testing at CSM ASPPRC
-
Transient metallurgical and physical response to rapid thermal processing
- Gleeble (resistance heater capable of 10 k Cps)
- Dilatometers (induction heating system with 1 k Cps)
-
Quenchant characterization
- Inverse Calculations
- Numerous mechanical property and microstructural analysis tools
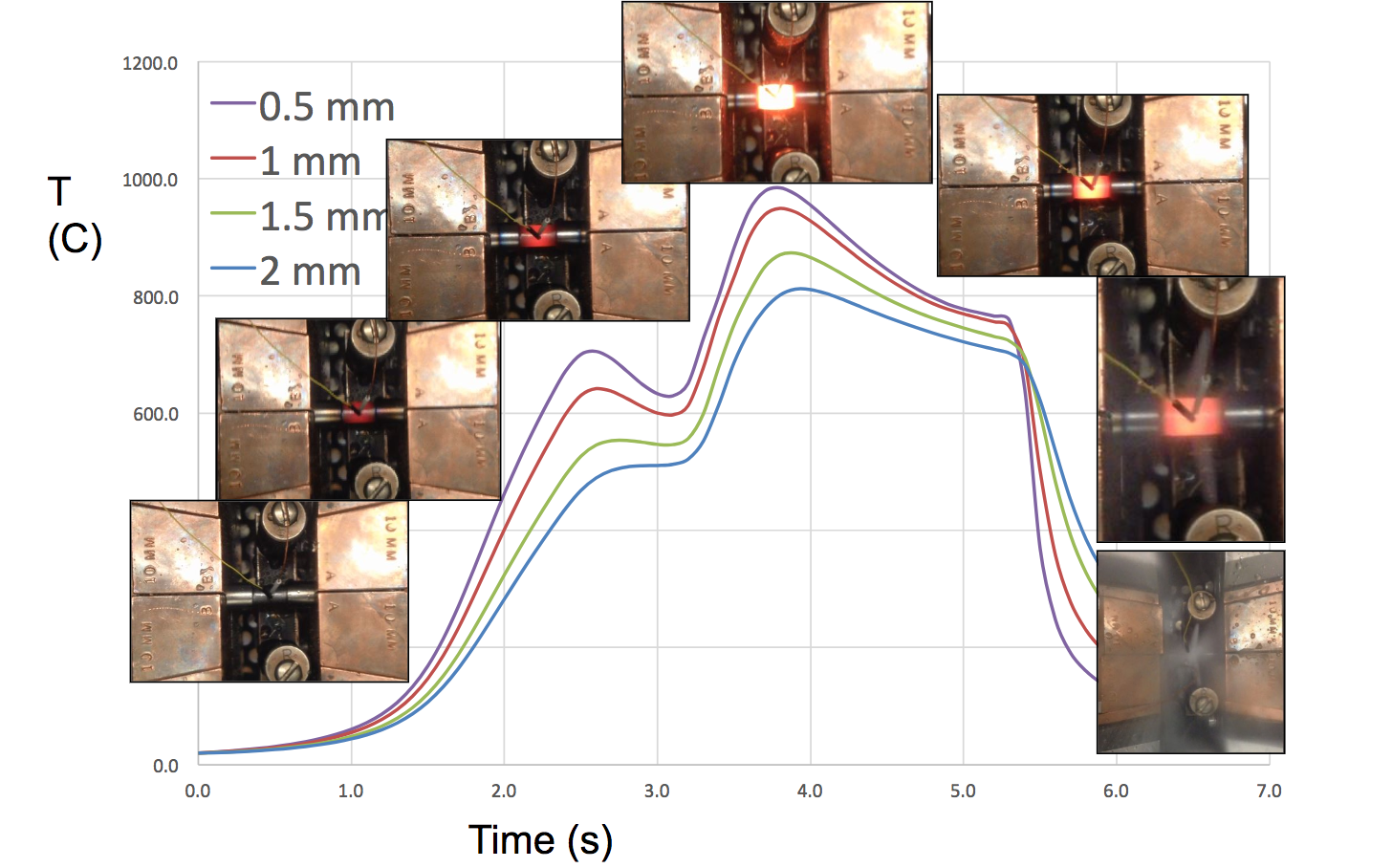
Comparison of Gleeble Tests with Computer Simulation using Flux
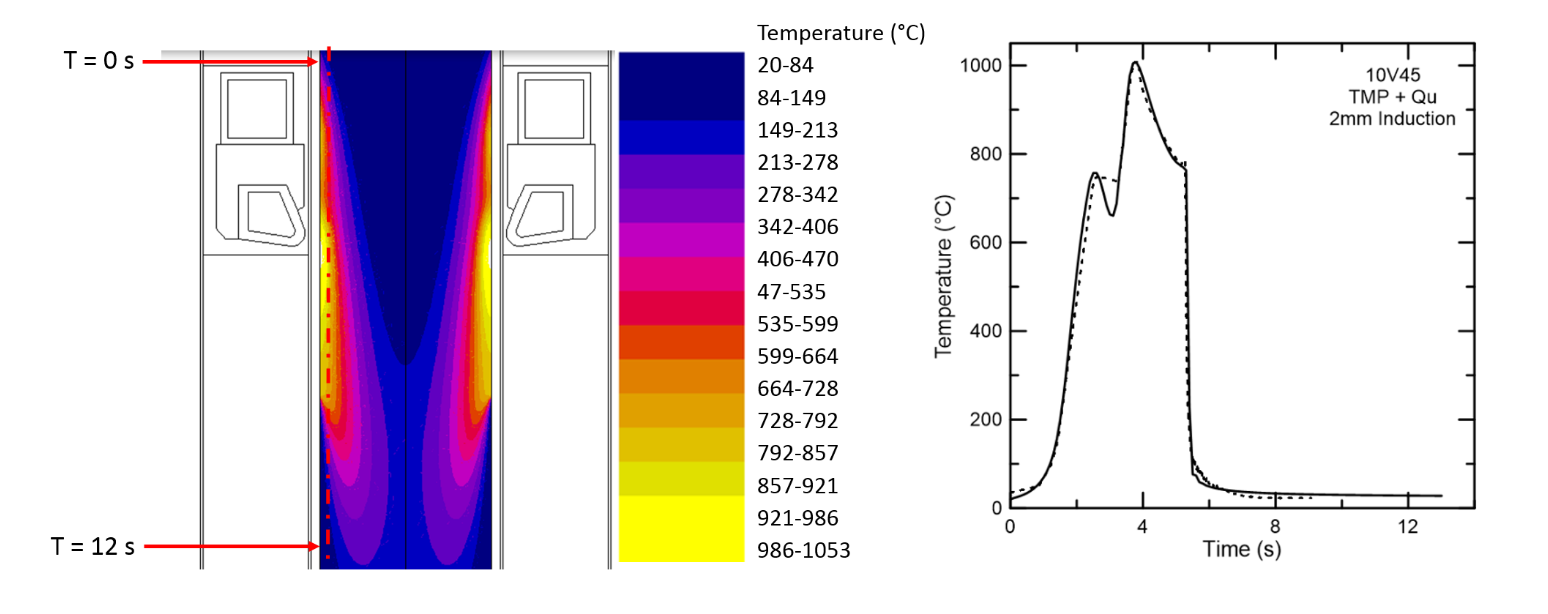
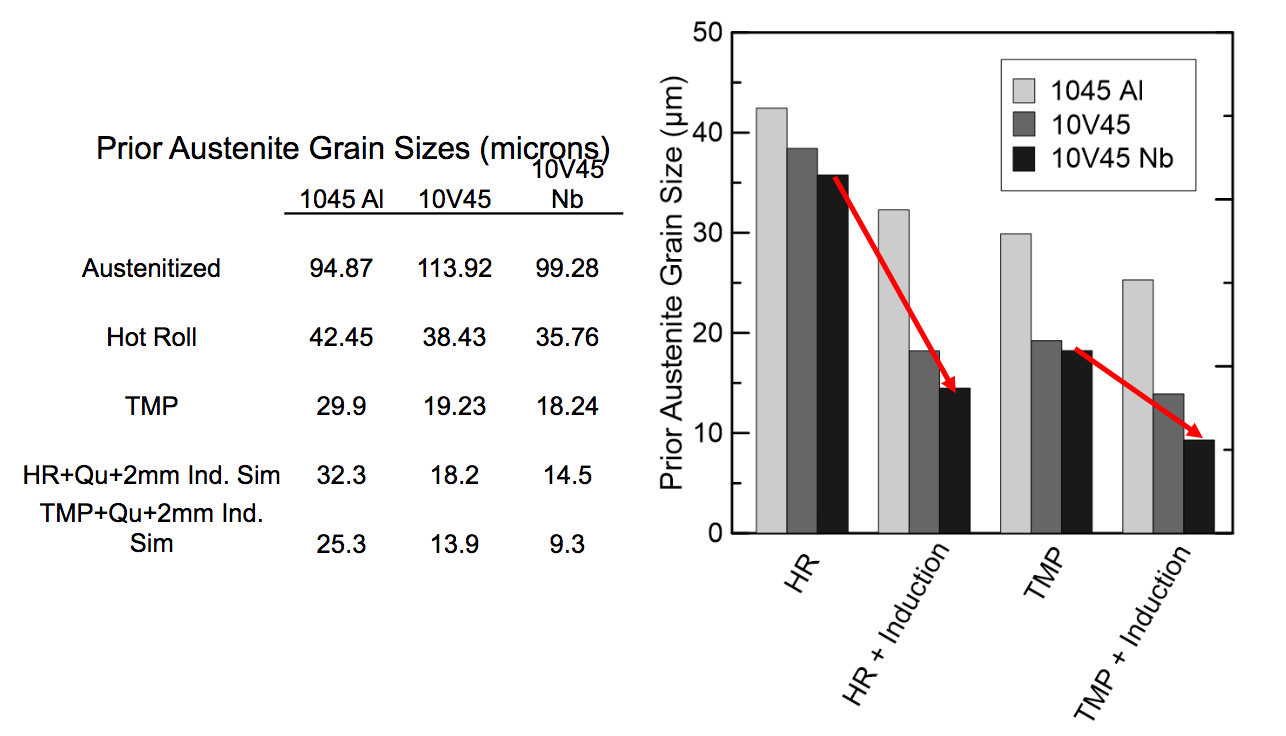
Induction Hardening – Gleeble Simulation
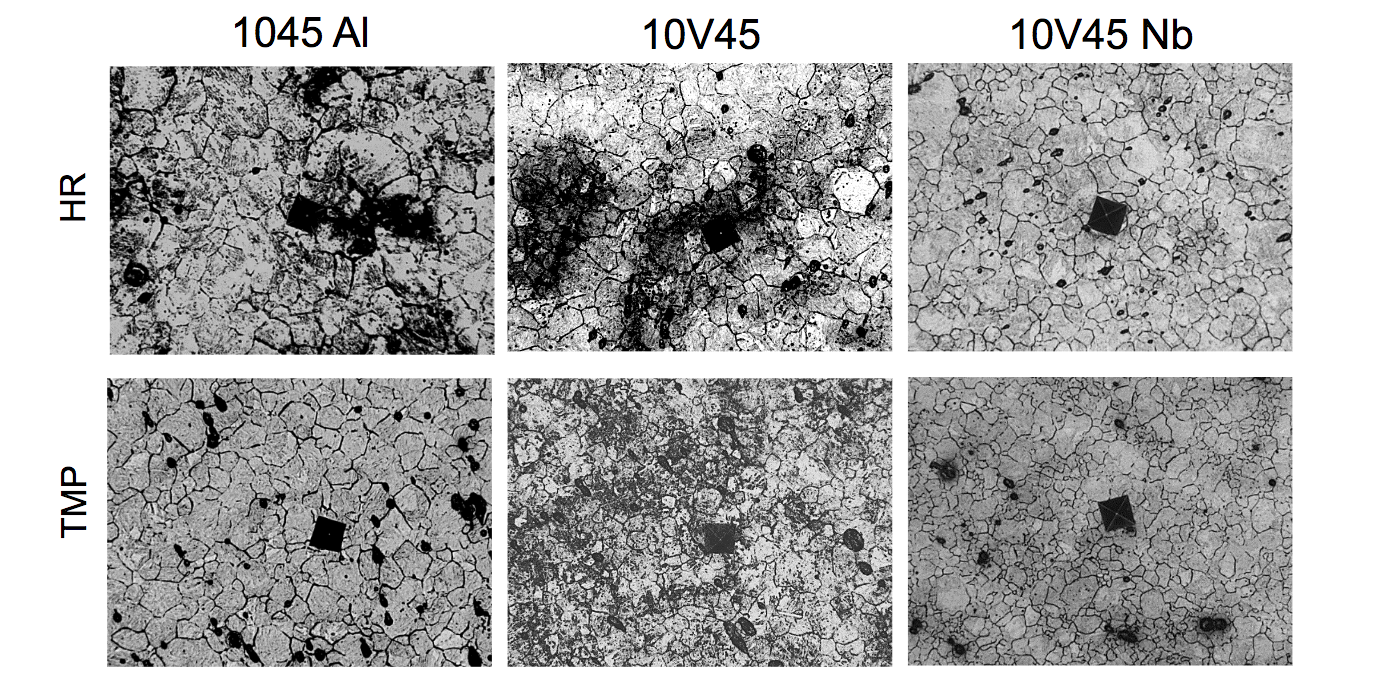
Post Induction Hardening PAGs (Direct Quench Conditions)
Induction Hardening – Gleeble Simulation
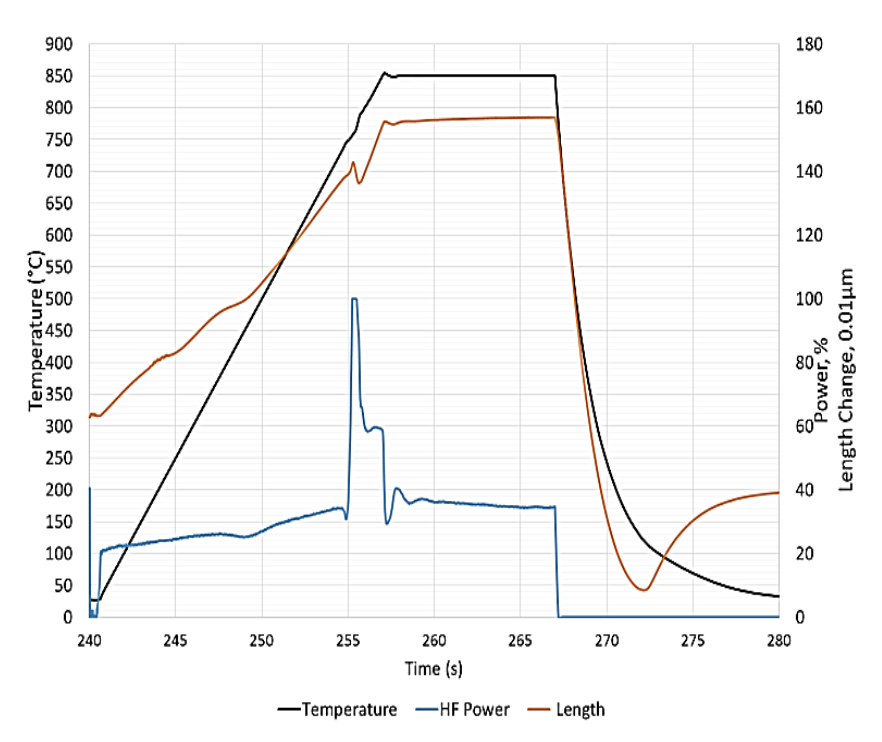
Dilatometer Testing
- 4 mm tool steel sample
-
Proposed cycle
- 50 Cps heating rate
- 850 C target temperature
- Hold at 850 C for 10 s
- Helium quench
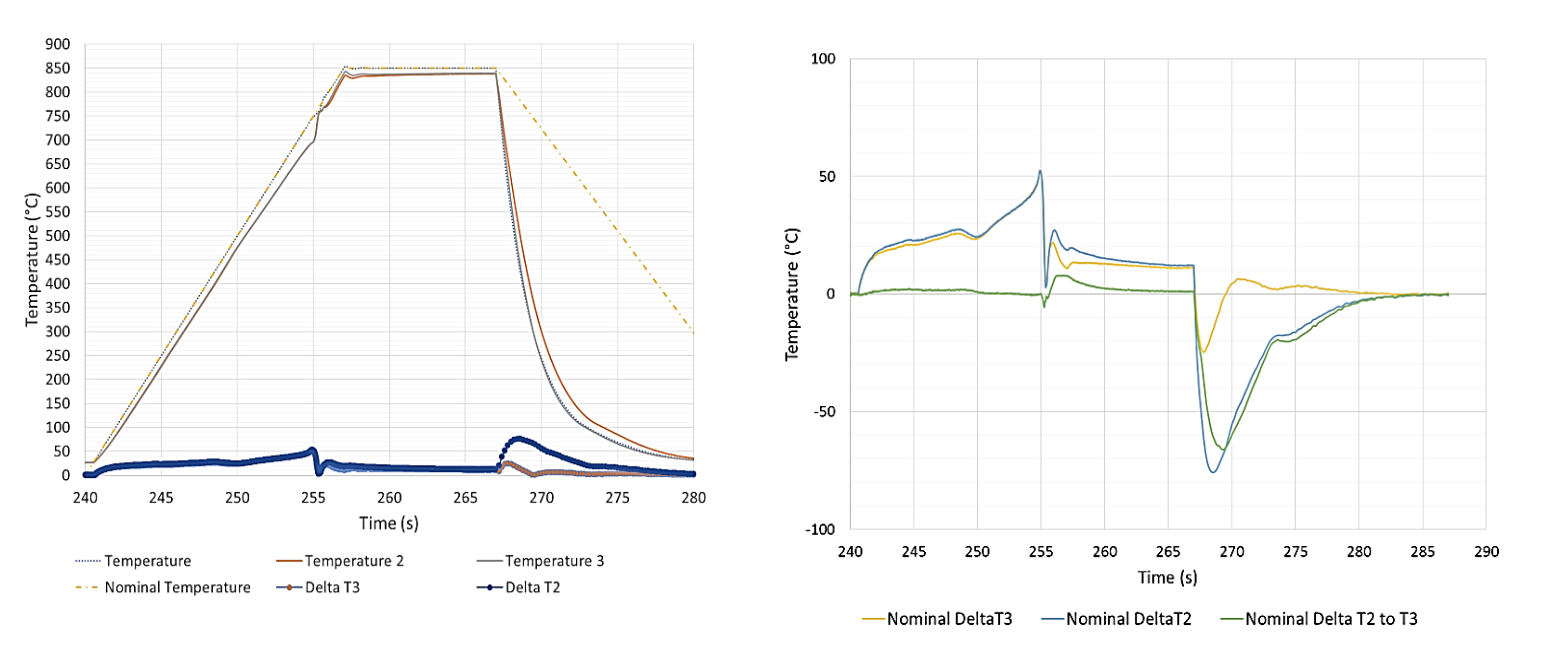
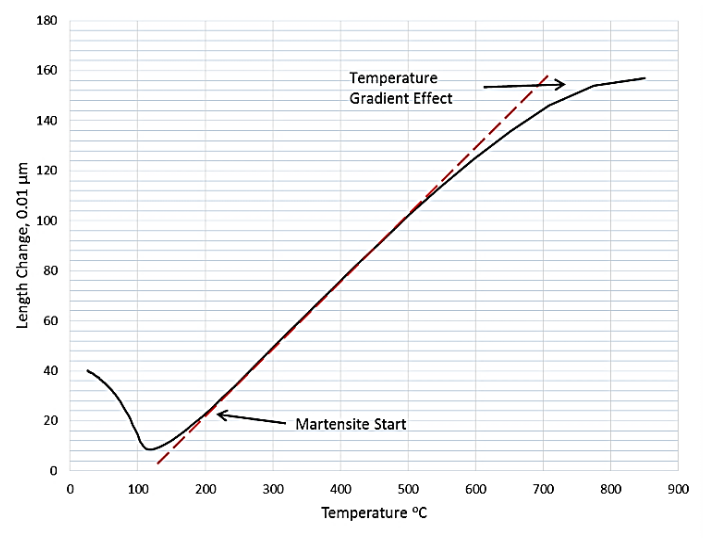
End to End Gradients in Sample Temperature During Trials
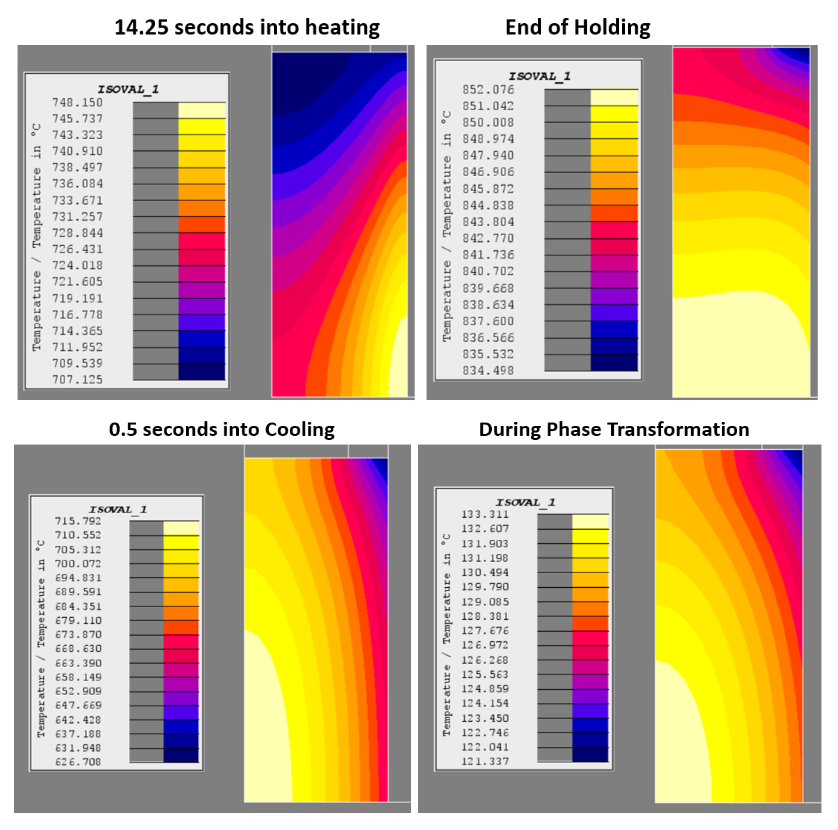
Modeled Temperature Distributions Agree with Test Results
Conclusions
- Induction heating is a widely used technology for heat treating
- Many induction heat treated components are known to have superior properties compared to components heat treated using other technologies, however, exactly why they perform as well as they do in some conditions is not fully understood
- Despite the widespread use of the technology, the materials database for induction heat treating needs to be improved to maximize the potential of the technology
- It is important to couple experimental tools with computer models to understand true temperature dynamics in the samples to properly interpret experimental results
Acknowledgements
- Some of the slides in this presentation were taken from the “Basics of Induction Heating Parts I & II” prepared by Dr. Valentin Nemkov (www.fluxtrol.com)
- Video Courtesy of Inductoheat (www.inductoheat.com)
- Physical Simulation Data provided by Advanced Steel Products and Processing Center at Colorado School of Mines
If you have more questions, require service or just need general information, we are here to help.
Our knowledgeable Customer Service team is available during business hours to answer your questions in regard to Fluxtrol product, pricing, ordering and other information. If you have technical questions about induction heating, material properties, our engineering and educational services, please contact our experts by phone, e-mail or mail.
Fluxtrol Inc.
1388 Atlantic Boulevard,
Auburn Hills, MI 48326
Telephone: +1-800-224-5522
Outside USA: 1-248-393-2000
FAX: +1-248-393-0277